Differences Between Rental Car and Personal Car Laws
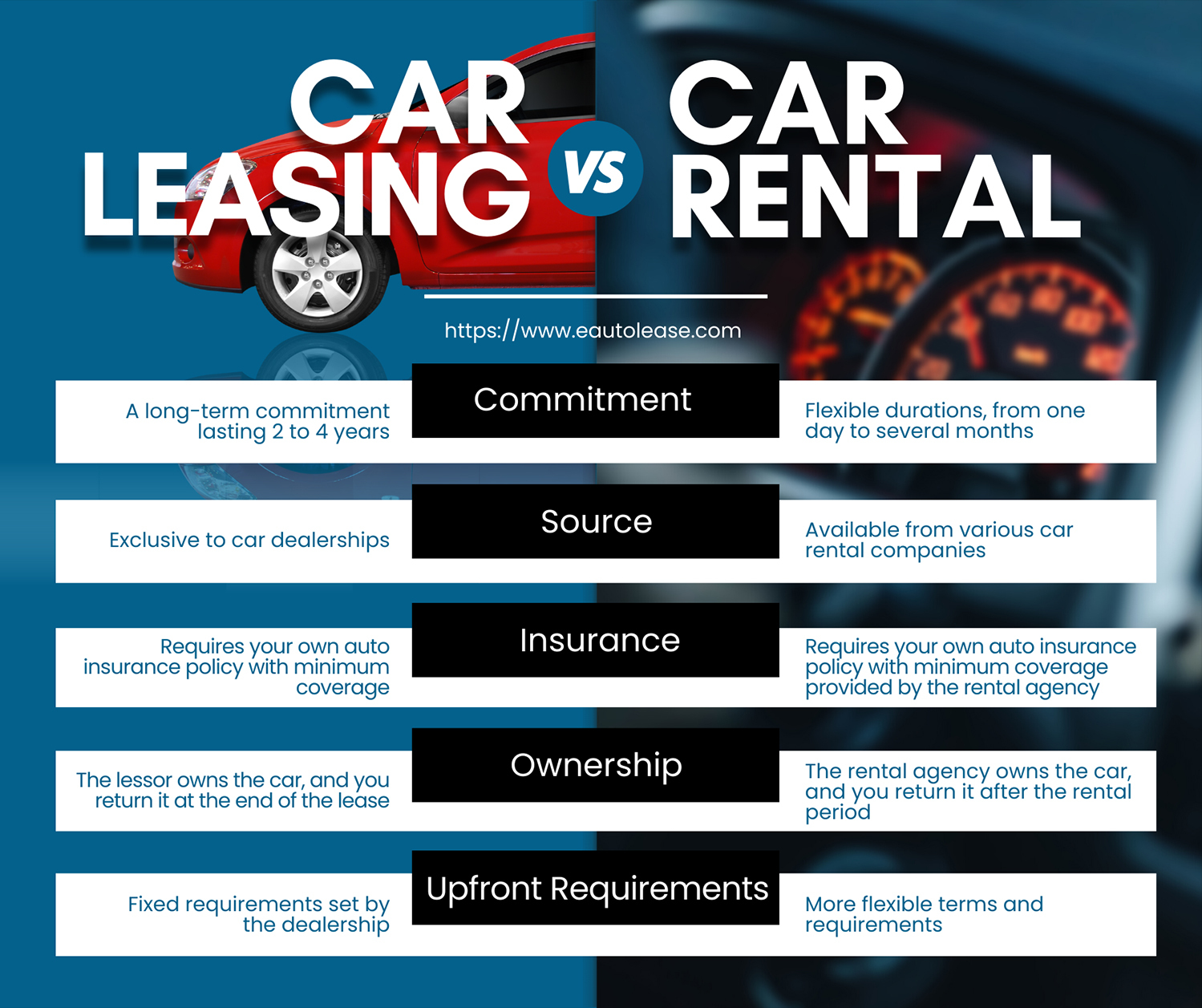
Driving in a new country is exciting! Imagine cruising down scenic routes, discovering hidden gems, and experiencing a culture firsthand. But before you buckle up, it's crucial to understand that the rules of the road might be different from what you're used to. A rental car doesn’t magically exempt you from local laws, and ignorance isn't an excuse.
Navigating foreign traffic rules can feel daunting, but it’s the key to a safe and enjoyable trip. Understanding the distinctions between rental car agreements and the local legal requirements will help you avoid hefty fines, potential accidents, and unnecessary stress. Think of it as preparing for any adventure – a little knowledge goes a long way!
One immediate step you can take is to research the basic traffic laws of your destination country. A quick online search for "[Country Name] driving laws" will give you a head start. Familiarize yourself with speed limits, right-of-way rules, and any specific regulations that might apply.
Navigating the Differences: Rental Car vs. Personal Car Laws
Renting a car abroad provides freedom and flexibility, but it also places you squarely under the jurisdiction of the host country's driving laws. While the rental agreement outlinesyourresponsibilities to the rental company, local laws dictate your obligations to theauthoritiesand other road users. These can be vastly different from what you’re used to at home. Let's break down the key areas where these differences manifest:
Jurisdiction and Enforcement
With a personal car, you're usually familiar with the laws of your home region. You know where speed cameras are often located, the general attitude of law enforcement, and the nuances of local driving customs. When renting a car in a foreign country, you step into a completely new legal environment. Foreign traffic rules are enforced by local authorities, and they don't typically offer leniency to tourists simply because they're unfamiliar with the regulations. This includes everything from speeding to parking violations and even smaller infractions like improper lane usage.
Rental Agreement vs. Local Law: The rental agreement outlines the terms and conditions of your rental, including insurance coverage and liability for damage to the vehicle. However, itdoesn'tsupersede local traffic laws. You are still responsible for adhering to all traffic regulations, regardless of what the rental agreement says. Consequences of Violations: Violating traffic laws can result in fines, points on your (potentially foreign) driving record, and even the impoundment of the rental car. In some countries, serious offenses can lead to arrest and imprisonment. The rental company may also charge you administrative fees for handling traffic violations incurred during your rental period. Cross-border Travel Considerations:If you plan on cross-border travel with your rental car, be aware that different countries have different laws. A practice that is legal in one country may be illegal in another. For instance, the required safety equipment might differ, or certain types of radar detectors might be prohibited. Always research the specific laws of each country you plan to visit.
Required Documentation and Equipment
Driving your own car usually means you have all the necessary documentation readily available: your driver's license, registration, and insurance information. Renting a car introduces additional factors.
Driver’s License and International Driving Permit (IDP): While your domestic driver’s license might be sufficient in some countries, many require an international driving permit (IDP), especially if your license is not in the local language. An IDP is essentially a translation of your driver's license and is recognized in many countries worldwide. It's crucial to check the specific requirements of the country you're visitingbeforeyou travel. Don’t leave home without it. Rental Agreement: Always keep a copy of the rental agreement in the car. It serves as proof that you have the right to be driving the vehicle. Vehicle Registration and Insurance: The rental company is responsible for providing the necessary vehicle registration and insurance documentation. Ensure these are readily accessible in the vehicle. Required Equipment: Many countries mandate specific safety equipment in vehicles, such as a reflective safety vest, a warning triangle, and a first-aid kit. Rental companies are usually required to provide these, but it's always a good idea to verify that they are present and in good condition before you drive off the lot.
Insurance Coverage
Understanding insurance coverage is vital, both with a personal vehicle and a rental car. However, the nuances of international car rental insurance can be complex.
Rental Car Insurance Options: Rental companies typically offer various insurance options, including collision damage waiver (CDW), theft protection, and liability insurance. It's essential to understand what each type of coverage entails and whether it adequately protects you in the event of an accident or theft. Personal Car Insurance Coverage Abroad: Check with your personal car insurance provider to see if your policy extends coverage to rental cars in foreign countries. Some policies offer limited coverage, while others provide no coverage at all. Credit Card Insurance:Some credit cards offer rental car insurance benefits when you use the card to pay for the rental. However, these benefits often have limitations and may require you to decline the rental company's insurance coverage. Read the terms and conditions of your credit card insurance policy carefully to ensure you understand the coverage and any exclusions. It's usually secondary coverage meaning it will only kick inafteryour primary insurance is exhausted.
Traffic Laws and Customs
Traffic laws and customs vary significantly from country to country. Failing to adhere to these differences can lead to accidents and legal trouble.
Right-of-Way Rules: Right-of-way rules can differ dramatically. For example, roundabouts are common in Europe, and understanding how to navigate them is crucial. In some countries, priority is given to vehicles entering the roundabout, while in others, it's given to vehicles already circulating. Speed Limits: Speed limits are usually posted in kilometers per hour (km/h) in most countries outside the United States. Pay close attention to speed limit signs and be aware that speed limits may vary depending on the type of road and the area (e.g., urban vs. rural). Parking Regulations: Parking regulations can be complex and strictly enforced. Pay attention to parking signs and meters, and avoid parking in restricted areas. Illegally parked vehicles are often towed, and you'll be responsible for paying the towing and storage fees. Driving Under the Influence (DUI) Laws: DUI laws are often stricter in other countries than in your home country. Even a small amount of alcohol in your system can result in severe penalties. It's always best to avoid drinking any alcohol before driving. Local Driving Customs:Observe local driving customs and adapt your driving style accordingly. For example, in some countries, drivers are more aggressive, while in others, they are more courteous. Be aware of these differences and adjust your behavior to fit in with the local driving culture.
Do I need an international driving permit?
An international driving permit (IDP) is often required, especially if your driver's license isn't in the local language. It translates your license information, making it easier for authorities to understand. Check the specific requirements of the country you're visiting before your trip. You can typically obtain an IDP from your local automobile association. It’s valid for a fixed period, usually one year. Remember, an IDP is a supplement to your existing driver's license,nota replacement. You must carry both documents when driving abroad.
What documents should I carry when driving abroad?
When driving abroad, carry the following documents:
Your valid driver's license from your home country
An international driving permit (IDP), if required
A copy of the rental agreement
Vehicle registration documents (provided by the rental company)
Proof of insurance (provided by the rental company)
Your passport
Keep these documents readily accessible in the vehicle. It's also a good idea to have digital copies stored on your phone or in the cloud in case the originals are lost or stolen.
How do police handle tourists on the road?
While law enforcement officers are generally professional, they are not always lenient with tourists who violate traffic laws. Ignorance of the law is not an excuse, and you'll be held accountable for your actions. If you are pulled over by the police, remain calm and respectful. Present your documents promptly and answer their questions honestly. Avoid arguing or becoming defensive. If you don't understand what they are saying, ask them to explain it clearly or to provide a translator. In some countries, it's common for police officers to issue on-the-spot fines for minor traffic violations. Be sure to get a receipt for any fine you pay.
Taking the time to understand the differences between rental car agreements and local driving laws can significantly enhance your travel experience. It's about more than just avoiding fines; it's about ensuring your safety and the safety of others on the road. Global road safety depends on everyone knowing and respecting the rules.
Armed with knowledge and a respectful attitude, you can confidently navigate the roads of any country. Embrace the adventure, but always remember that responsible driving is the key to unlocking a world of unforgettable experiences. Enjoy the journey, and drive safely!
Posting Komentar untuk "Differences Between Rental Car and Personal Car Laws"